MedSearch is an old-school Create, Read, Update, Delete (“CRUD”) Java DatabaseConnectivity (“JDBC”) MySQL application built in the Eclipse IDE, which I worked on with a team while learning about MySql databases. JDBC essentially is a Java API used to execute queries on a database. It was my first time integrating a MySql database into a project. Initially, our project was deployed: the MySql database was hosted on AWS server and accessed virtually with DBeaver, and the code and server were local. There are many features for regular users of the system and for administrators of the system, so we will only review a few.
FEATURES:
1. Creation Features
A new User can be registered and added to the system. New drugs can be added. Below is a section of the user creation form.

2. Read Features
Certain drugs and drug services can be searched for.
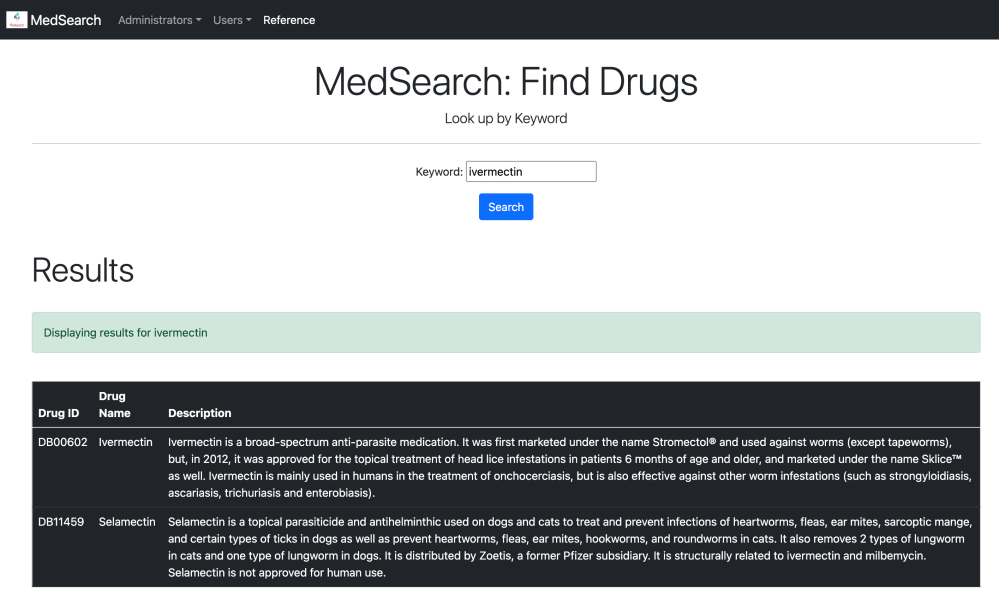
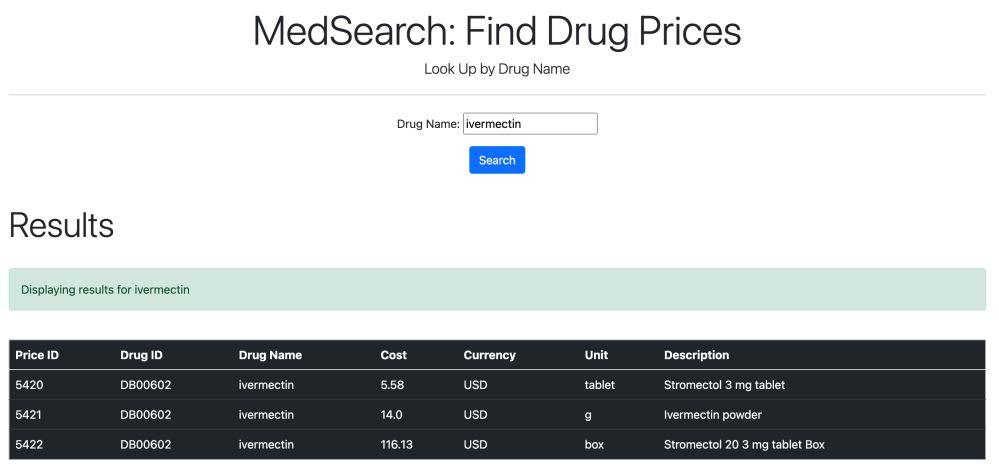
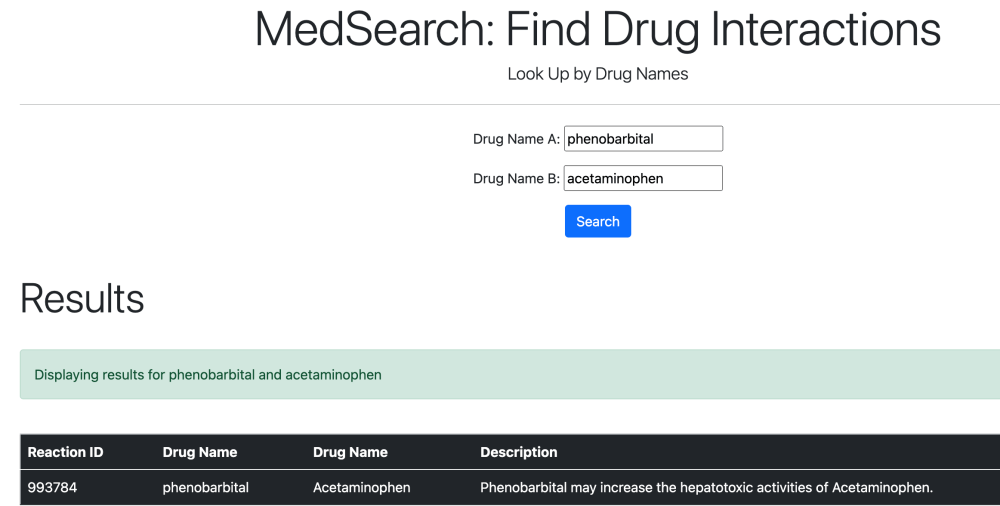
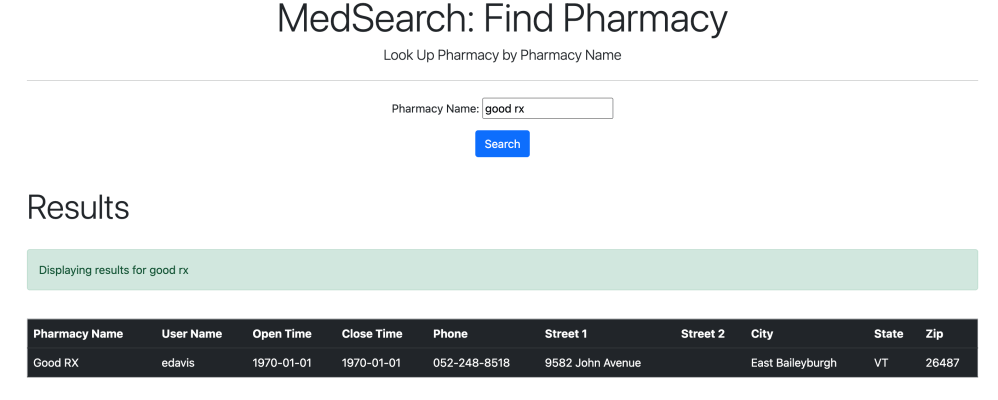
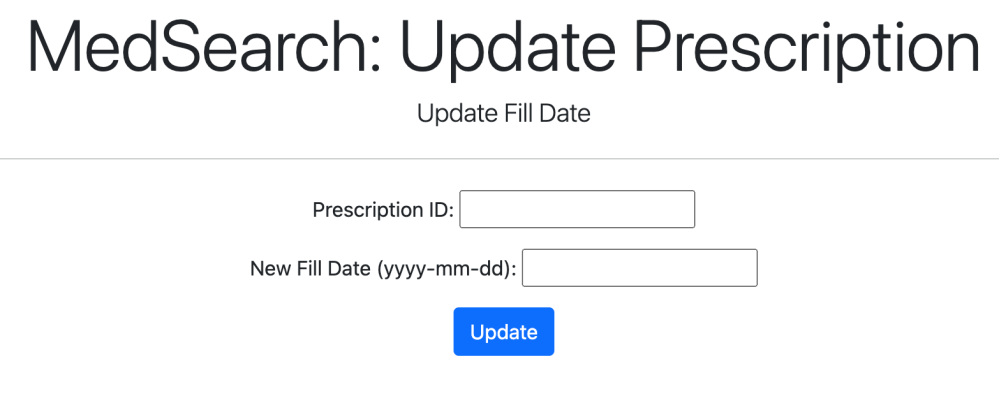
3. Update Features
Information can be changed, for instance, prescription fill dates of prescriptions already entered into the database.
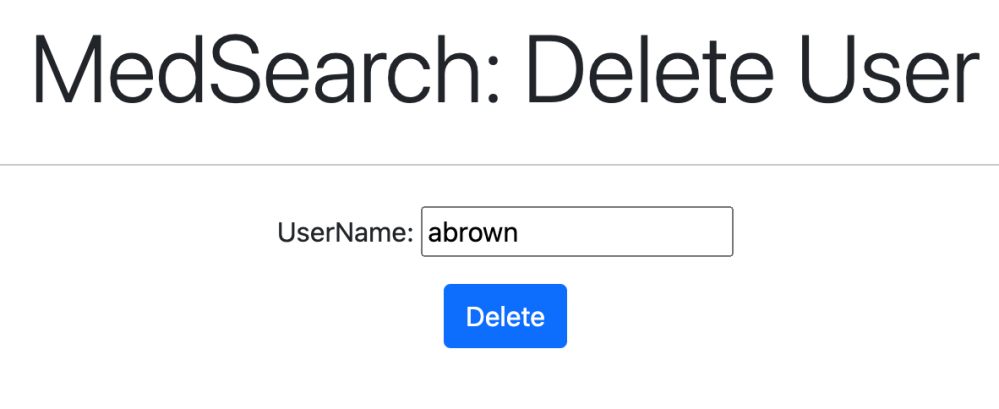
4. Delete Features
Administrators can delete Users from the system.
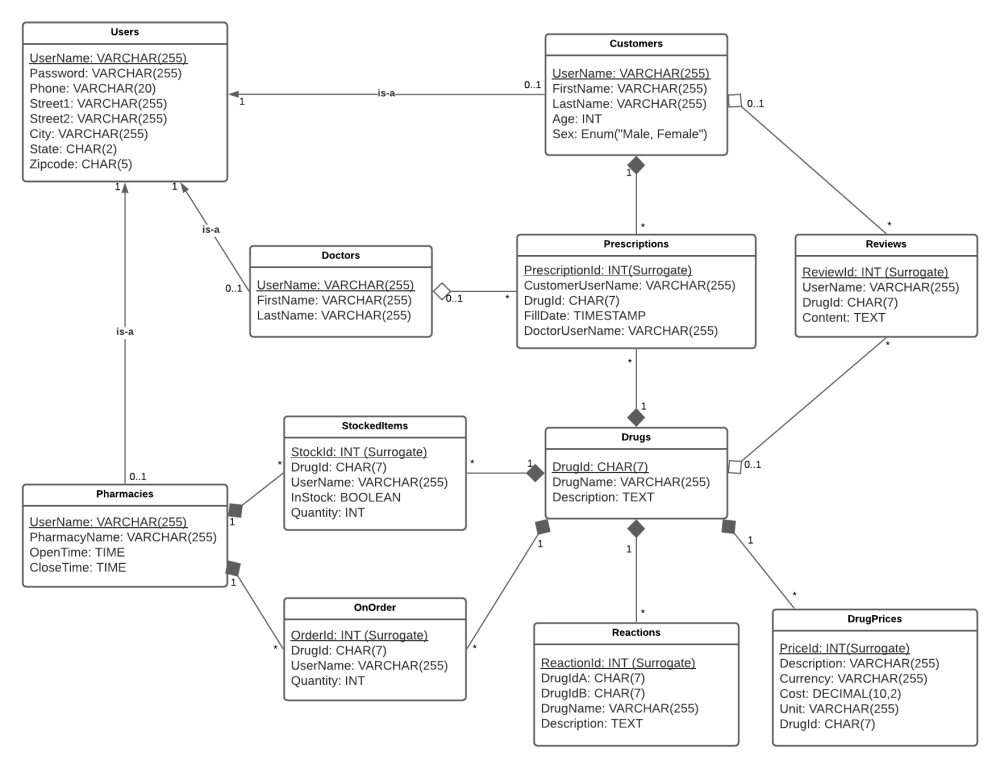
Database
In this sort of project, which lacks a modern Framework, the MVC architecture is more obvious and apparent than, for instance, a Spring project, where Hibernate does a lot of work.
The complex table schema was planned via a UML before the tables were then created in MySql:

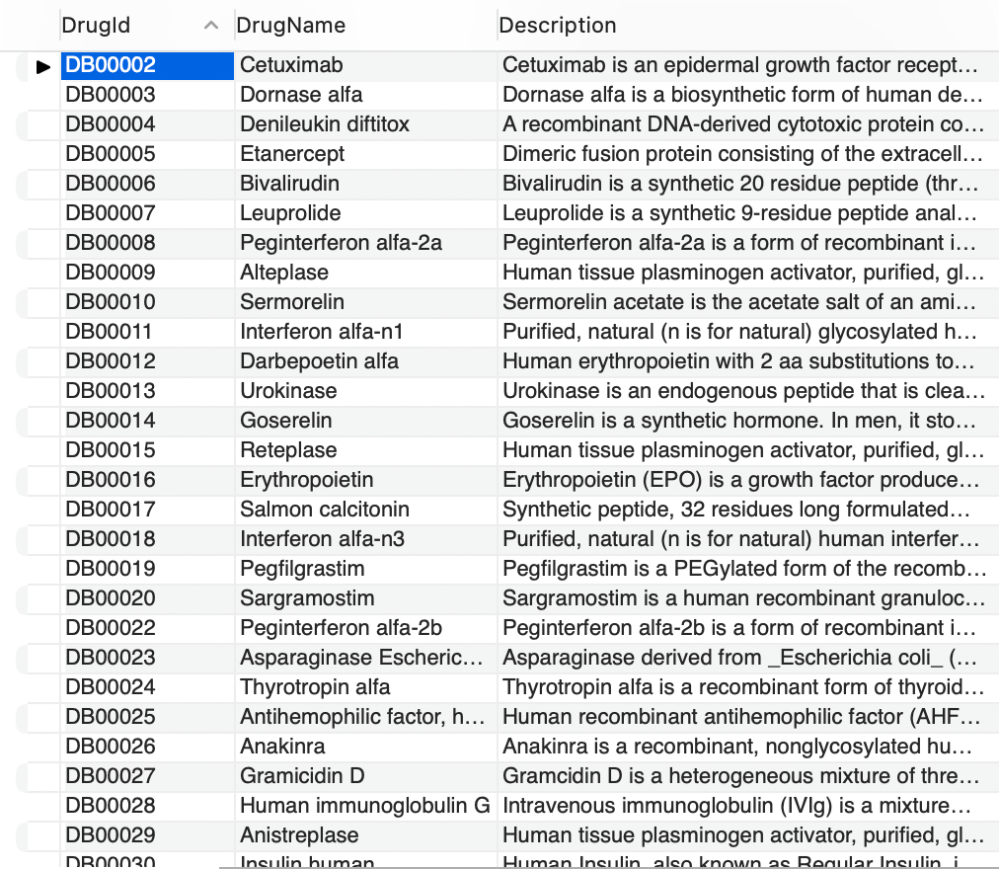
The tables were then occupied via MySQL. This project heavily relied on data from .csv files, which was prepared and cleaned:

Here is an except from the simple Drugs table, as an example:
MVC Arcitectures
Overview
From the View .jsp pages, a user of the website may send various HTTP requests to a servlet/controller. Then the servlet controller handles the HTTP request and generally feteches a DAO from the model layer. The DAO model, empty, retrieves its data from the database and returns it to the servlet class (the controller). Finally, the controller sends the response objects to the JSP for display.
1. The Model Layer
The Model consisted of Data Access Objects (DAOs) which provides CRUD operations for each table in the database, based on a plain old java object(POJO)/ data transfer object. There is no “Repository” to interact with the database and retrieve the data like there is in a Spring project; each DAO must be created painstakingly. In Spring, the data returned and the POJO serve as the model layer.
The Drugs data transfer object class and DrugsDAO class, for instance, are part of the Model Layer


2. The View Layer
The View consisted of many .jsp pages with HTML and css. CreateDrug.jsp was one such page, which utilized a post method in a HTML form to communicate with the appropriate server/controller.

3. The Controller Layer
Servlet controller classes exist for each endpoint and rely on the functions of the DAO of the model layer. FindDrugs class is one such controller.

Closing Remarks
Creating a JDBC CRUD Application was a great way to practice MVC architecture in a web application and to create a complex table schema. It also gave me a chance to work directly with the connectionManager Java interface and the Tomcat server environment and write different code than I would for a React or Spring project.
View the project on my Github:
https://github.com/zachasyl/MedSearch


Leave a comment